
The Antarctic-Arctic Radiation-belt (Dynamic) Deposition – VLF Atmospheric Research Konsortium (AARDDVARK) provides continuous long-range observations of the lower-ionosphere. The Konsortia sensors detect changes in ionisation levels from ~30-85 km altitude, with the goal of increasing the understanding of energy coupling between the Earth’s atmosphere, Sun, and Space. We use the upper atmosphere as a gigantic energetic particle detector to observe and understand changing energy flows; this Science area impacts our knowledge of global change, communications, and navigation. The joint NZ-UK Antarctic-Arctic Radiation-belt (Dynamic) Deposition – VLF Atmospheric Research Konsortia (AARDDVARK) is a new extension of a well-establish experimental technique, allowing long-range probing of ionisation changes at comparatively low altitudes. Most other instruments which can probe the same altitudes are limited to essentially overhead measurements. At this stage AARDDVARK is essentially unique, as similar systems are only deployed at a regional level.
Introduction
One of the few experimental techniques that can probe these altitudes uses very low-frequency (VLF) electromagnetic radiation, trapped between the lower ionosphere (~85 km) and the Earth; these signals can be received thousands of kilometres from the source. The nature of the received radio waves is determined by propagation inside the Earth-ionosphere waveguide, with variability largely coming from changes in the electron density profiles at and below the lower ionosphere. We have recently developed the AARDDVARK global-scale network of sensors that monitor fixed-frequency communications transmitters, and hence provide continuous long-range observations between the transmitter and receiver locations. Our receivers log small changes in the phase and amplitude of powerful VLF communications transmitters (~13-30 kHz). By monitoring distant VLF stations we undertake long-range remote sensing of changes to the waveguide, and particularly the ionosphere. For example solar flares lead to large changes to the daytime ionosphere, leading to changes in the propagation of the transmitter signals recorded by our instruments. We also study changes caused by electron precipitation from the Van Allen radiation belts, solar eclipses, and red sprites. We have written a brief tutorial describing how subionospheric propagation is used to remote sense the upper atmosphere. AARDDVARK is a Konsortium currently made up of:
British Antarctic Survey (BAS), United Kingdom
University of Otago, New Zealand (in part working with Antarctica New Zealand)
Kwa-Zulu Natal University, South Africa
Eötvös University, Hungary
University of Oulu, Finland (operating through the Sodankylä Geophysical Observatory)
University of Newcastle, Australia (operating with the Australian Antarctic Division)
University of Alberta, Canada
University of Lancaster, United Kingdom
Natural Resources Canada, Canada
A more detailed description as to how subionospheric VLF propagation can be used to for long range remote sensing can be found at the AARDDVARK Tutorial page.
The AARDDVARK Science Team is supporting the following research projects:
CHAMOS – CHemical Aeronomy in the Mesosphere and Ozone in the Stratosphere
IHY – International Heliophysical Year
CARISMA – Canadian Array for Realtime Investigations of Magnetic Activity
BARREL – Balloon Array for RBSP Relativistic Electron Losses
Data Policy
Each participating institute collects and holds its own AARDDVARK data in the form of observations and logs, etc. AARDDVARK members can request selected data periods for scientific study from one another. The exchange of AARDDVARK data between members of the Konsortia is undertaken with the goal of specific scientific projects. Data exchange is undertaken with the clear understanding that there will be co-authorship and consultation as to any publications making use of each member’s data.
Non-Konsortia members interested in AARDDVARK observations should communicate in the first instance with the AARDDVARK Principal Investigators (Clilverd and Rodger), who can identify which sensors are best suited for your requirements. All interpretation of AARDDVARK data should be undertaken by Konsortia members, who are experts in the understanding of these observations.
AARDDVARK: Sensing the Globe
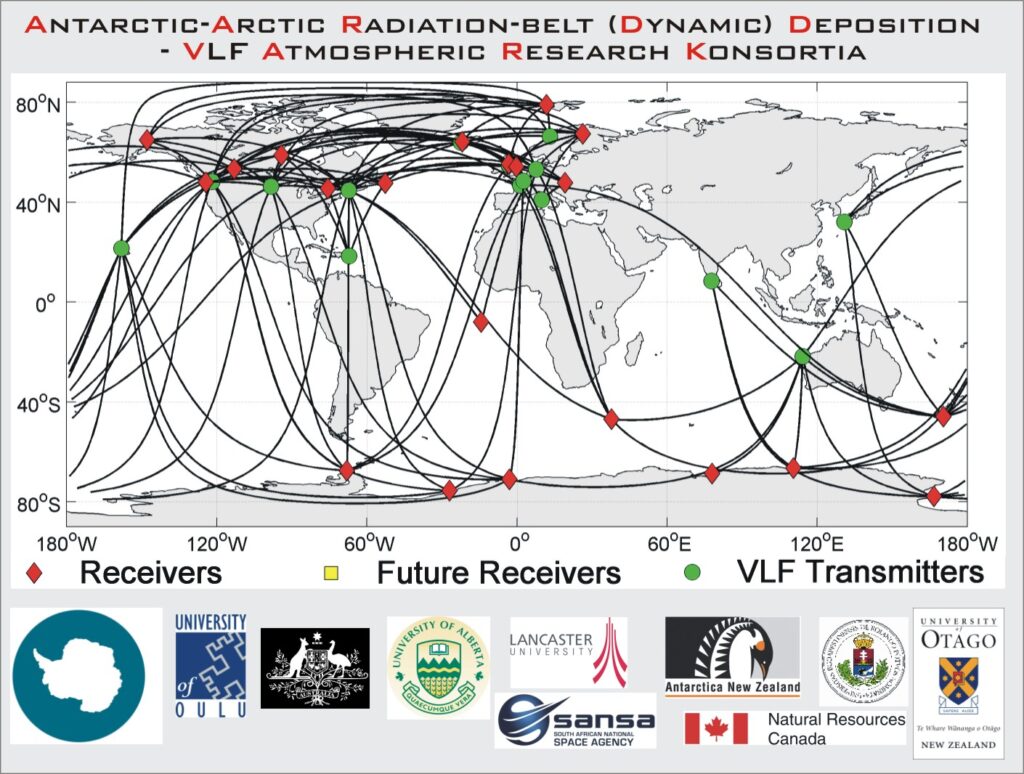
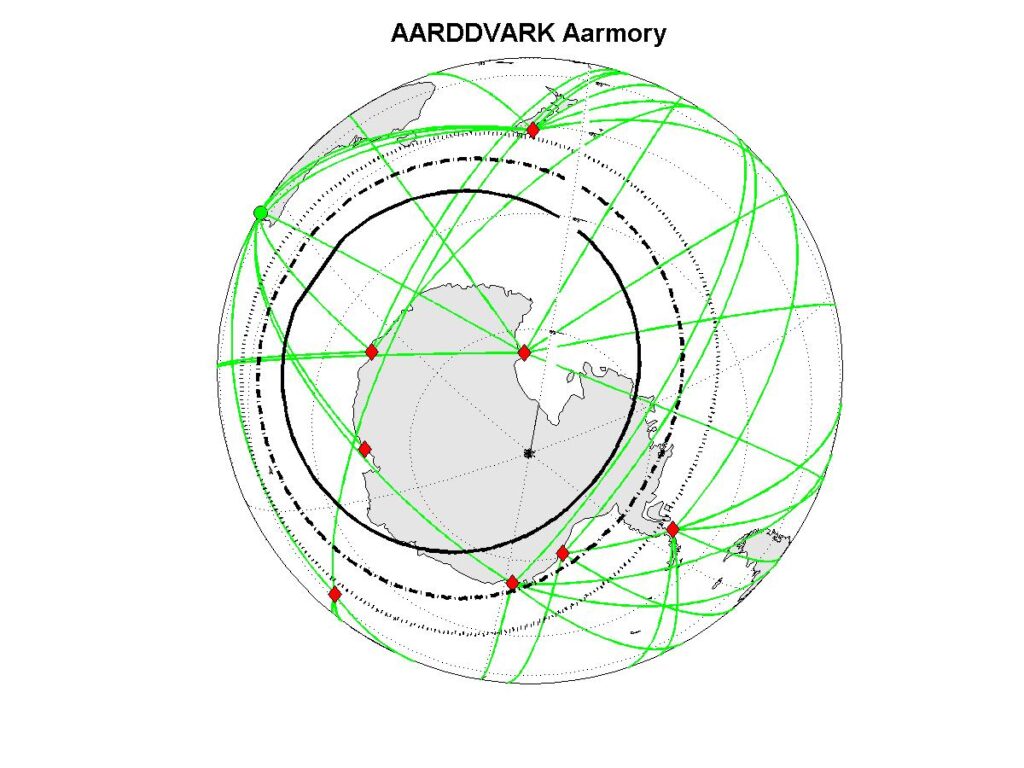
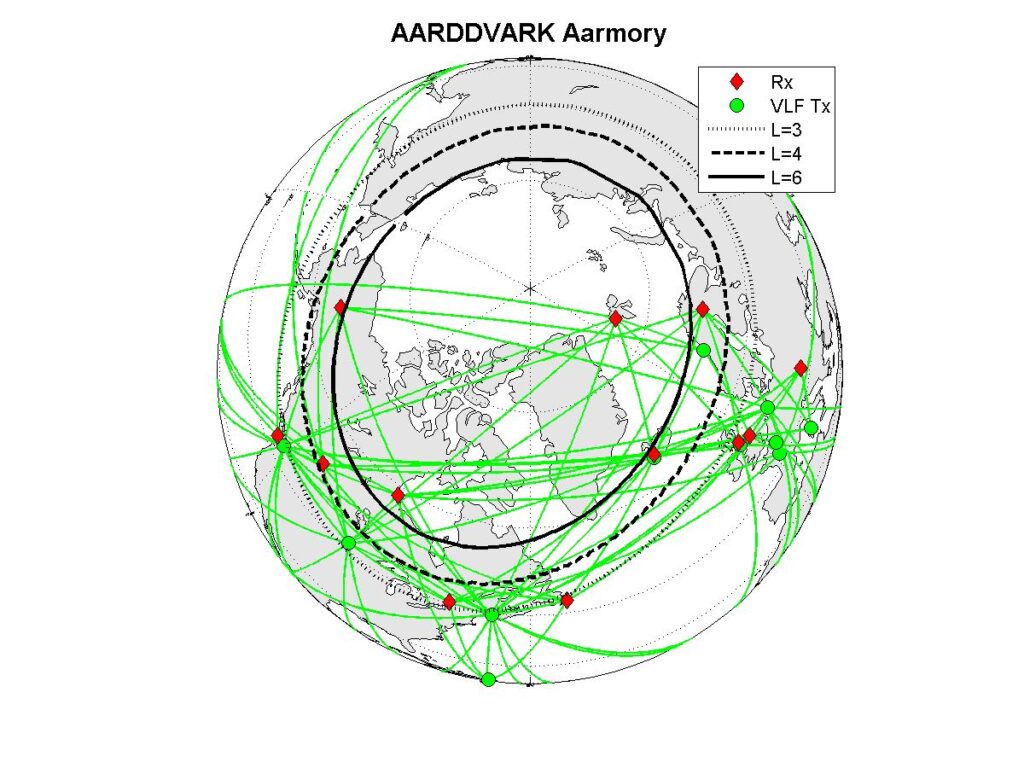
Most of our AARDDVARK sensors are deployed to monitor the Antarctic and Arctic regions. The plot above shows our existing AARDDVARK receiver (Rx) locations (red diamonds). The great circle paths between the monitored VLF communications transmitters (Tx, circles) and the receiver sites are also shown, which indicates the atmospheric areas monitored. Our planned AARDDVARK sensors for the future are shown as yellow squares. The AARDDVARK great circle plot map above has an indication of geomagnetic coordinates through the McIlwain L-shell‘s. It is often clearer to use polar maps to view the great circle paths at high latitudes. These are reproduced below in the same format.
Current AARDDVARK Science Topics
We are currently working on a number of active Science topics. Background information on each Science topic is given below, with the text normally drawn from the introduction of current papers:
- Whistler-induced Electron Precipitation
- Solar Proton Events
- Relativistic Electron Precipitation
- Decent of NOx from Thermospheric Altitudes
- Solar Flares
- References for the papers cited in the background material
AARDDVARK People
Principle Investigators
Mark Clilverd (British Antarctic Survey)
Craig Rodger (Otago University)A full listing of the people involved in the AARDDVARK network can be found on the AARDDVARK people webpage.
AARDDVARK Pictures
Images of our experimental sites at some locations are available. Many of our receivers are at picturesque locations around the world!
AARDDVARK Instrumentation
Operational AARDDVARK sensors vary from location to location. The majority are based upon the “OmniPAL” narrowband VLF receiver. Currently, ARDDVARK include the follow receiver types: OmniPAL, AbsPAL, VELOX AARDDVARK, UltraMSK. The AARDDVARK network was formed in January 2005. However, some of the sensors which make up the network were individually operational well before this date, while others have come on-line since.
| Halley | January 2006 (note historic data exists from this site) |
| Rothera | January 2006 (note historic data exists from this site) |
| Dunedin | May 2002 (note significant historic data exists from this site) |
| Erd | October 2003 (note significant historic data exists from this site) |
| Sodankylä | October 2002 |
| Ny Alesund | June 2003 |
| SANAE | January 2006 |
| Casey | April 2005 |
| Fort Churchill | May 2007 |
| Scott Base | December 2008 |
| Edmonton | October 2010 |
| Eskdalemuir | September 2011 |
| Forks | October 2011 |
| West Antarctica | January 2012 – January 2014 |
| Ottawa | September 2012 |
| St John’s | October 2012 |
| Reykjavik | May 2013 |
| Kamchatka | December 2012 -January 2014 (this is a WWLLN station which was running UltraMSK software to support the BARREL campaign) |
| Davis | December 2012 (this is a WWLLN station running UltraMSK software originally setup to support the BARREL campaign) |
| Fairbanks | December 2012 (this is a WWLLN station running UltraMSK software originally setup to support the BARREL campaign) |
| Ascension | December 2012 (this is a WWLLN station running UltraMSK software) |
Current VLF spectra spanning 0-24 kHz from the locations of our AARDDVARK sites are available over the internet courtesy of our collaborators in the WWLLN network. Spectra are available from the following WWLLN locations which also have AARDDVARK sensors:
These majority of these spectra are updated every 10 minutes and show the wideband VLF observations for 15 s after the timestamp.
AARDDVARK Publications
The AARDDVARK network has currently produced 73 papers in international peer reviewed journals. Looking for PDFs of these papers? Most of them can be downloaded from the Otago University Space Physics group publications website.
Beharrell, M. J., F. Honary, C. J. Rodger, and M. A. Clilverd, Substorm induced energetic electron precipitation: morphology and prediction, J. Geophys. Res., 120, 2993–3008, doi:10.1002/2014JA020632, 2015.
Belcher, S. R. G., M. A. Clilverd, C. J. Rodger, S. Cook, N. R. Thomson, J. B. Brundell, T. Raita, Solar flare X-ray impacts on long subionospheric VLF paths, Space Weather, 19, e2021SW002820, doi:10.1029/2021SW002820, 2021.
Clilverd, M. A., N. Cobbett, C. J. Rodger, J. B. Brundell, M. Denton, D. Hartley, J. Rodriguez, D. Danskin, T. Raita, and E. L. Spanswick, Energetic electron precipitation characteristics observed from Antarctica during a flux dropout event, J. Geophys. Res., 118, doi:10.1002/2013JA019067, 2013.
Clilverd, M. A., R. Duthie, R. Hardman, A. T. Hendry, C. J. Rodger, T. Raita, M. Engebretson, M. R. Lessard, D. Danskin, and D. K. Milling, Electron precipitation from EMIC waves: a case study from 31 May 2013, J. Geophys. Res., 120, 3618–3631, doi: 10.1002/2015JA021090, 2015.
Clilverd, M. A., R. Duthie, C. J. Rodger, R. L. Hardman, and K. Yearby, Long-term climate change in the D-region, Sci. Rep., 7:16683, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-16891-4, 2017.
Clilverd, M. A., C. J. Rodger, Th. Ulich, A. Seppälä, E. Turunen, A. Botman, and N. R. Thomson, Modelling a large solar proton event in the southern polar cap, J. Geophys. Res., 110(A9), doi: 10.1029/2004JA010922, 2005.
Clilverd, M. A., C. J. Rodger and Th. Ulich, The importance of atmospheric precipitation in storm-time relativistic electron flux drop outs, Geophys. Res. Lett., 33, L01102, doi:10.1029/2005GL024661, 2006.
Clilverd, M. A., C. J. Rodger, R. M. Millan, J. G. Sample, M. Kokorowski, M. P. McCarthy, Th. Ulich, T. Raita, A. J. Kavanagh, and E. Spanswick, Energetic particle precipitation into the middle atmosphere triggered by a coronal mass ejection, J. Geophys. Res., 112, A11210, doi:10.1029/2007JA012395, 2007.
Clilverd, M. A., C. J. Rodger, J. B. Brundell, N. Cobbett, J. Bähr, T. Moffat-Griffin, A. J. Kavanagh, A. Seppälä, N. R. Thomson, R. H. W. Friedel, and F. W. Menk, Energetic electron precipitation during sub-storm injection events: high latitude fluxes and an unexpected mid-latitude signature, J. Geophys. Res., 113, A10311, doi: 10.1029/ 2008JA013220, 2008.
Clilverd, M. A., C. J. Rodger, N. R. Thomson, J. B. Brundell, Th. Ulich, J. Lichtenberger, N. Cobbett, A. B. Collier, F. W. Menk, A. Seppälä, P. T. Verronen, and E. Turunen, Remote sensing space weather events: the AARDDVARK network, Space Weather, 7, S04001, doi:10.1029/2008SW000412, 2009.
Clilverd, M. A., C. J. Rodger, R. J. Gamble, Th. Ulich, T. Raita, A. Seppälä, J. C. Green, N. R. Thomson, J. A. Sauvaud, and M. Parrot, Ground-based estimates of outer radiation belt energetic electron precipitation fluxes into the atmosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 115, A12304, doi:10.1029/2010JA015638, 2010.
Clilverd, M. A., C. J. Rodger, S. Dietrich, T. Raita, Th. Ulich, E. Clarke, A. W. P. Thomson, and A. J. Kavanagh, High latitude geomagnetically induced current events observed on very low frequency radio wave receiver systems, Radio Sci., 45(2), RS2006, doi:10.1029/2009RS004215, 2010.
Clilverd, M. A., C. J. Rodger, T. Moffat-Griffin, E. Spanswick, P. Breen, F. W. Menk, R. S. Grew, K. Hayashi, I. R. Mann, Energetic outer radiation-belt electron precipitation during recurrent solar activity, J. Geophys. Res., 115, A08323, doi:10.1029/2009JA015204, 2010.
Clilverd, M. A., C. J. Rodger, I. J. Rae, J. B. Brundell, N. R. Thomson, N. Cobbett, P. T. Verronen, and F. W. Menk, Combined THEMIS and ground-based observations of a pair of substorm associated electron precipitation events, J. Geophys. Res., 117, A02313, doi:10.1029/2011ja016933, 2012.
Clilverd, M. A., C. J. Rodger, M. McCarthy, R. Millan, L. Blum, N. Cobbett, J. B. Brundell, D. Danskin and A. J. Halford, Investigating energetic electron precipitation energy spectra through combining ground-based, and balloon observations, J. Geophys. Res., 122, 534–546, doi:10.1002/2016JA022812, 2017.
Clilverd, M. A., C. J. Rodger, D. Danskin, M. E. Usanova, T. Raita, Th. Ulich, and E. L. Spanswick, Energetic Particle injection, acceleration, and loss during the geomagnetic disturbances which upset Galaxy 15, J. Geophys. Res., 117, A12213, doi:10.1029/2012JA018175, 2012.
Clilverd, M. A., C. J. Rodger, M. van de Kamp, and P. T. Verronen, Electron precipitation from the outer radiation belt during the St Patrick’s Day storm 2015: observations, modelling, and validation, J. Geophys. Res., 125, e2019JA027725, doi:10.1029/2019JA027725, 2020.
Clilverd, M. A., A. Seppälä , C. J. Rodger, N. R. Thomson, J. Lichtenberger, and P. Steinbach, Temporal variability of the descent of high-altitude NOX, J. Geophys. Res., 112, A09307, doi:10.1029/2006JA012085, 2007.
Clilverd, M. A., A. Seppälä, C. J. Rodger, N. R. Thomson, P. T. Verronen, E. Turunen, Th. Ulich, J. Lichtenberger, and P. Steinbach, Modeling polar ionospheric effects during the October-November 2003 solar proton events, Radio Sci., 41(2), doi: 10.1029/2005RS003290, 2006.
Clilverd, M. A., A. Seppälä, C. J. Rodger, P. T. Verronen, and N. R. Thomson, Ionospheric evidence of thermosphere-to-stratosphere descent of polar NOX, Geophys. Res. Lett., 33, L19811, doi:10.1029/2006GL026727, 2006.
Clilverd, M. A., A. Seppälä, C. J. Rodger, M. G. Mlynczak, and J. U. Kozyra, Additional stratospheric NOx production by relativistic electron precipitation during the 2004 spring NOx descent event, J. Geophys. Res., 114, A04305, doi:10.1029/2008JA013472, 2009.
Cresswell-Moorcock, K., C. J. Rodger, M. A. Clilverd, D. Milling, Techniques to determine the quiet day curve for a long-period of subionospheric VLF observations, Radio Sci., 50, 453–468, 2015.
Dietrich, S. L., C. J. Rodger, M. A. Clilverd, J. Bortnik, and T. Raita, Relativistic microburst storm characteristics: combined satellite and ground-based observations, J. Geophys. Res., 115, A12240, doi:10.1029/2010JA015777, 2010.
Gamble, R. J., C. J. Rodger, M. A. Clilverd, J. A. Sauvaud, N. R. Thomson, S. L. Stewart, R. J. McCormick, M. Parrot, and J.-J. Berthelier, Radiation belt electron precipitation by manmade VLF transmissions, J. Geophys. Res, 113, A10211, doi: 10.1029/2008JA013369, 2008.
Gamble, R. J., C. J. Rodger, M. A. Clilverd, J. A. Sauvaud, N. R. Thomson, S. L. Stewart, R. J. McCormick, M. Parrot, and J.-J. Berthelier, Correction to “Radiation belt electron precipitation by man-made VLF transmissions”, J. Geophys. Res., 114, A05205, doi:10.1029/2009JA014304, 2009.
George, H., C. J. Rodger, M. A. Clilverd, K. Cresswell-Moorcock, J. B. Brundell, and N. R. Thomson, Developing a nowcasting capability for X-Class solar flares using VLF radiowave propagation changes, Space Weather, 17, 1783-1799, doi:10.1029/2019SW002297, 2019.
Gokani, S. A., M. Kosch, M. A. Clilverd, C. J. Rodger, and A. K. Sinha, What fraction of the outer radiation belt relativistic electron flux at L≈3-4.5 was lost to the atmosphere during the dropout event of the St Patrick’s Day storm of 2015?, J. Geophys. Res., 124, 9537-9551, doi:10.1029/2018JA026278, 2019.
Hardman, R., M. A. Clilverd, C. J. Rodger, J. B. Brundell, R. Duthie, R. H. Holzworth, I. R. Mann, D. K. Milling, and E. Macusova, A case study of electron precipitation fluxes due to plasmaspheric hiss, J. Geophys. Res., 120, 6736–6748, doi:10.1002/2015JA021429, 2015.
Hendry, A. T., M. A. Clilverd, C. J. Rodger, and M. J. Engebretson, Ground-based VLF observations of EPP, in The Dynamic Loss of Earth’s Radiation Belts: From Loss in the Magnetosphere to Particle Precipitation in the Atmosphere, edited by Maria Usanova and Allison Jaynes, Chapter 8, 257-277, Elsevier, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813371-2.00008-1, ISBN: 9780128133712, 2019.
Hendry, A. T., C. J. Rodger, M. A. Clilverd, N. R. Thomson, S. K. Morley, T. Raita, Rapid radiation belt losses occurring during high-speed solar wind stream–driven storms: Importance of energetic electron precipitation, in Dynamics of the Earth’s Radiation Belts and Inner Magnetosphere, Geophys. Monogr. Ser., vol. 199, edited by D. Summers et al., 213–223, AGU, Washington, D. C., doi:10.1029/2012GM001299, 2013.
Hendry, A. T., C. J. Rodger, M. A. Clilverd, M. J. Engebretson, I. R. Mann, M. R. Lessard, T. Raita, and D. K. Milling, Confirmation of EMIC wave driven relativistic electron precipitation, J. Geophys. Res., 121, 5366–5383, doi:10.1029/2015JA022224, 2016.
Hendry, A. T., O. Santolik, Y. Miyoshi, A. Matsuoka, C. J. Rodger, M. A. Clilverd, C. A. Kletzing, M. Shoji, and I. Shinohara, A multi-instrument approach to determining the source-region extent of EEP-driving EMIC waves, Geophys. Res. Lett. , 47, e2019GL086599, doi:10.1029/2019GL086599, 2020.
Lichtenberger, J., M. A. Clilverd, B. Heilig, M. Vellante, J. Manninen, C. J. Rodger, A. B. Collier, A. M. Jorgensen, J. Reda, R. H. Holzworth, R. Friedel, and M. Simon- Wedlund, The plasmasphere during a space weather event: First results from the PLASMON, J. Space Weather Space Climate, 3 (A3), http://dx.doi.org/10.1051/swsc/2013045, 2013.
Macotela, E. L., M. A. Clilverd, J. Manninen, T. Moffat-Griffin, D. A. Newnham, T. Raita, and C. J. Rodger, D-region high latitude forcing factors, J. Geophys. Res., 124, 765–781, doi:10.1029/2018JA026049, 2019.
Miyoshi, Y., S. Oyama, S. Saito, S. Kurita, H. Fujiwara, R. Kataoka, Y. Ebihara, C. Kletzing, G. Reeves, O. Santolik, M. Clilverd, C. J. Rodger, E. Turunen, and F. Tsuchiya, Energetic electron precipitation associated with pulsating aurora: EISCAT and Van Allen Probe observations, J. Geophys. Res., 120, 2754–2766, doi: 10.1002/2014JA020690, 2015.
Neal, J. J., C. J. Rodger, M. A. Clilverd, N. R. Thomson, T. Raita, and Th. Ulich, Long-term determination of energetic electron precipitation into the atmosphere from AARDDVARK subionospheric VLF observations, J. Geophys. Res., 120, 2194–2211, doi:10.1002/2014JA020689, 2015.
Newnham, D. A., P. J. Espy, M. A. Clilverd, C. J. Rodger, A. Seppälä, D. J. Maxfield, P. Hartogh, K. Holmén, and R. B. Horne, Observations of nitric oxide in the Antarctic middle atmosphere during recurrent geomagnetic storms, J. Geophys. Res., doi:10.1002/2013JA019056, 2013.
Nunn, D., M. A. Clilverd, C. J. Rodger, and N. R. Thomson, The impact of PMSE and NLC particles on VLF propagation, Ann. Geophys., 22(5), 1563-1574, 2004.
Oyama, S., A. Kero, C. J. Rodger, M. A. Clilverd, Y. Miyoshi, N. Partamies, E. Turunen, T. Raita, P. T. Verronen, and S. Saito, Energetic electron precipitation and auroral morphology at the substorm recovery phase, J. Geophys. Res., doi:101002/2016JA023484, 6508–6527, 2017.
Rodger, C. J., and R. J. McCormick, Remote sensing of the upper atmosphere by VLF, in Sprites, Elves and Intense Lightning Discharges: Proceedings of the NATO Advanced Study Institute from 21-30 July 2004, edited by M. Füllekrug, Nato Science Series II (Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry), Vol. 225, Hardcover ISBN 1-4020-4627-8, Springer, 2006.
Rodger, C. J., A. T. Hendry, M. A. Clilverd, C. A. Kletzing, J. B. Brundell, and G. D. Reeves, High-resolution in-situ observations of electron precipitation-causing EMIC Waves, Geophys. Res. Lett., 42, 9633–9641, doi:10.1002/2015GL066581, 2015.
Rodger, C. J., B. R. Carson, S. A. Cummer, R. J. Gamble, M. A. Clilverd, J-A. Sauvaud, M. Parrot, J. C. Green, and J.-J. Berthelier, Contrasting the efficiency of radiation belt losses caused by ducted and non-ducted whistler mode waves from ground-based transmitters, J. Geophys. Res., 115, A12208, doi:10.1029/2010JA015880, 2010.
Rodger, C. J., M. A. Clilverd, N. R. Thomson, D. Nunn, and J. Lichtenberger, Global prediction of inner radiation belt energy deposition caused by lightning, Annales Geophys., 23(11), 3419-3430, 2005.
Rodger, C. J., M. A. Clilverd, Th. Ulich, P. T. Verronen, E. Turunen, and N. R. Thomson, The atmospheric implications of Radiation Belt Remediation, Annales Geophys., 24(7), 2025 – 2041, SRef-ID: 1432-0576/ag/2006-24-2025, 2006.
Rodger, C. J., M. A. Clilverd, D. Nunn, P. T. Verronen, J. Bortnik, and E. Turunen, Storm-time short-lived bursts of relativistic electron precipitation detected by subionospheric radio wave propagation, J. Geophys. Res., 112, A07301, doi:10.1029/2007JA012347, 2007.
Rodger, C. J., M. A. Clilverd, N. R. Thomson, R. J. Gamble, A. Seppälä, E. Turunen, N. P. Meredith, M. Parrot, J. A. Sauvaud, and J.-J. Berthelier, Radiation belt electron precipitation into the atmosphere: recovery from a geomagnetic storm, J. Geophys. Res., 112, A11307, doi:10.1029/2007JA012383, 2007.
Rodger, C. J., M. A. Clilverd, A. Seppälä, N. R. Thomson, R. J. Gamble, M. Parrot, J. A. Sauvaud and Th. Ulich, Radiation belt electron precipitation due to geomagnetic storms: significance to middle atmosphere ozone chemistry, J. Geophys. Res., 115, A11320, doi:10.1029/2010JA015599, 2010.
Rodger, C. J., M. A. Clilverd, A. J. Kavanagh, C. E. J. Watt, P. T. Verronen, and T. Raita, Contrasting the responses of three different ground-based instruments to energetic electron precipitation, Radio Sci., 47(2), RS2021, doi:10.1029/2011RS004971, 2012.
Rodger, C. J., C. F. Enell, E. Turunen, M. A. Clilverd, N. R. Thomson, and P. T. Verronen, Lightning-driven inner radiation belt energy deposition into the atmosphere: Implications for ionisation-levels and neutral chemistry, Annales Geophys., 25, 1745-1757, 2007.
Rodger, C. J., T. Raita, M. A. Clilverd, A. Seppälä, S. Dietrich, N. R. Thomson, and Th. Ulich, Observations of relativistic electron precipitation from the radiation belts driven by EMIC Waves, Geophys. Res. Lett., 35, L16106, doi:10.1029/2008GL034804, 2008.
Seppälä, A., M. A. Clilverd, and C. J. Rodger, NOx enhancements in the middle atmosphere during 2003-2004 polar winter: Relative significance of solar proton events and the aurora as a source, J. Geophys. Res., D23303, doi:10.1029/2006JD008326, 2007.
Seppälä, A., M. A. Clilverd, C. J. Rodger, P. T. Verronen, and E. Turunen, The effects of hard spectra solar proton events on the middle atmosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 113, A11311, 2008.
Seppälä, A., P. T. Verronen, V. F. Sofieva, J. Tamminen, E. Kyrölä C. J. Rodger, and M. A. Clilverd, Destruction of the tertiary ozone maximum during a solar proton event, Geophys. Res. Lett., 33, L07804, doi:10.1029/2005GL025571, 2006.
Silber, I., C. Price, C. J. Rodger, and C. Haldoupis, Links between mesopause temperatures and ground-based VLF narrowband radio signals, J. Geophys. Res., 118, doi:10.1002/jgrd.50379, 2013.
Silber, I., C. G. Price, and C. J. Rodger, Semi-annual oscillation (SAO) of the nighttime ionospheric D-region as detected through ground-based VLF receivers, Atmos. Chem. Phys., 16, 3279–3288, doi:10.5194/acp-16-3279-2016, 2016.
Simon Wedlund, M., M. A. Clilverd, C. J. Rodger, K. Cresswell-Moorcock, N. Cobbett, P. Breen, D. Danskin, E. Spanswick, and J. V. Rodriguez, A statistical approach to determining energetic outer radiation-belt electron precipitation fluxes, J. Geophys. Res., 119, 3961–3978, doi:10.1002/2013JA019715, 2014.
Thomson, N. R., M. A. Clilverd, J. B. Brundell, and C. J. Rodger, Quiet night Arctic ionospheric D region characteristics, J. Geophys. Res., 126, e2020JA029043, doi:10.1029/2020JA029043, 2021.
Thomson, N. R., M. A. Clilverd, W. M. McRae, Nighttime ionospheric D region parameters from VLF phase and amplitude, J. Geophys. Res., 112, A07304, doi:10.1029/2007JA012271, 2007.
Thomson, N. R., M. A. Clilverd, and C. J. Rodger, Daytime Mid-Latitude D-region Parameters at Solar Minimum from Short Path VLF Phase and Amplitude, J. Geophys. Res., 116, A03310, doi:10.1029/2010JA016248, 2011.
Thomson, N. R., M. A. Clilverd, and C. J. Rodger, Ionospheric D region: VLF-measured Electron Densities compared with Rocket-Based FIRI-2018 Model, J. Geophys. Res., 127, e2022JA030977, doi:10.1029/2022JA030977, 2022.
Thomson, N. R., M. A. Clilverd, and C. J. Rodger, Ionospheric D region: Characteristics near Dawn and Dusk, J. Geophys. Res., 130, e2024JA033610, doi:10.1029/2024JA033610, 2025.
Thomson, N. R., and W. M. McRae, Nighttime ionospheric D region: Equatorial and Non-equatorial, J. Geophys. Res., 114, A8, doi:10.1029/2008JA014001, 2009.
Thomson, N. R., C. J. Rodger, and M. A. Clilverd, Large solar flares and their ionospheric D-region enhancements, J. Geophys. Res., 110, A06306, doi:10.1029/2005JA011008, 2005.
Thomson, N. R., C. J. Rodger, and R. L. Dowden, Ionosphere gives size of greatest solar flare, Geophys. Res. Lett., 31(6), L06803, 10.1029/2003GL019345, 2004.
Thomson, N. R., C. J. Rodger, and M. A. Clilverd, Daytime D-region Parameters from Long Path VLF Phase and Amplitude, J. Geophys. Res., 116, A11305, doi:10.1029/2011JA016910, 2011.
Thomson, N. R., C. J. Rodger, and M. A. Clilverd, Tropical Daytime Lower D-region Dependence on Sunspot Number, J. Geophys. Res., 117(A10), A10306, doi:10.1029/2012JA018077, 2012.
Thomson, N. R., M. A. Clilverd, and C. J. Rodger, Low Latitude Ionospheric D-region Dependence on Solar Zenith Angle, J. Geophys. Res., 119, 6865–6875, doi:10.1002/2014JA020299, 2014.
Thomson, N. R., M. A. Clilverd, and C. J. Rodger, Midlatitude ionospheric D region: height, sharpness and solar zenith angle, J. Geophys. Res., 122, 8933–8946, doi:10.10029/2017JA024455, 2017.
Thomson, N. R., M. A. Clilverd, and C. J. Rodger, Quiet daytime Arctic ionospheric D region, J. Geophys. Res., 123, doi:10.1029/2018JA025669, 9726–9742, 2018.
Turunen, E., P. T. Verronen, A. Seppälä, C. J. Rodger, M. A. Clilverd, J. Tamminen, C. F. Enell and Th. Ulich, Impact of different precipitation energies on NOX generation during geomagnetic storms, J. Atmos Sol.-Terr. Phys., 71, pp. 1176-1189, doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2008.07.005, 2009.
van de Kamp, M., A. Seppälä, M. A. Clilverd, C. J. Rodger, P. T. Verronen, and I. Whittaker, A model providing long-term datasets of energetic electron precipitation during geomagnetic storms, J. Geophys. Res., 121, 5366–5383, doi:10.1029/2015JA022224, 2016.
Verronen, P. T., C. J. Rodger, H. M. Pickett, M. A. Clilverd, and E. Turunen, Latitudinal extent of the January 2005 solar proton event in the Northern Hemisphere from satellite observations of hydroxyl, Annales Geophys., 25, 2203-2215, 2007.
Verronen , P. T., A. Seppälä, M. A. Clilverd, C. J. Rodger, E. Kyrölä C. F. Enell, Th. Ulich, and E. Turunen, Diurnal variation of ozone depletion during the October-November 2003 solar proton event, J. Geophys. Res., 110(A9), doi:10.1029/2004JA010932, 2005.
Zigman, V., M. Dominique, D. Grubor, C. J. Rodger, and M. A. Clilverd, Lower-ionosphere electron density and effective recombination coefficients from multi-instrument space observation and ground VLF measurements during solar flares, J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys., 247, 1-15, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2023.106074, 2023.
Looking for PDFs of these papers? Most of them can be downloaded from the Otago University Space Physics group publications website. [last updated 10 Nov 2022]
AARDDVARK Presentations
A listing of AARDDVARK conference presentations and seminars is available. Please contact Craig Rodger if this listing needs to be updated.
